Here we are going to discuss about Locomotive Boiler: Definition, Working Principle, Components, Advantages and Applications (Notes with PDF). As we all know that Boiler is one of the major and most vital machine in any power plant industry.
So, stay tuned till end! You will get every detailed information about Locomotive Boiler.
What is Locomotive Boiler?
Table of Contents
The locomotive boiler is an axis of horizontal drum, draft work, natural circulation, multiple tubes, medium pressure, solid fuel burning internally fired boiler.
It is used in marine engines and railway locomotive engines. It is a mobile boiler and has a high level of steam production.
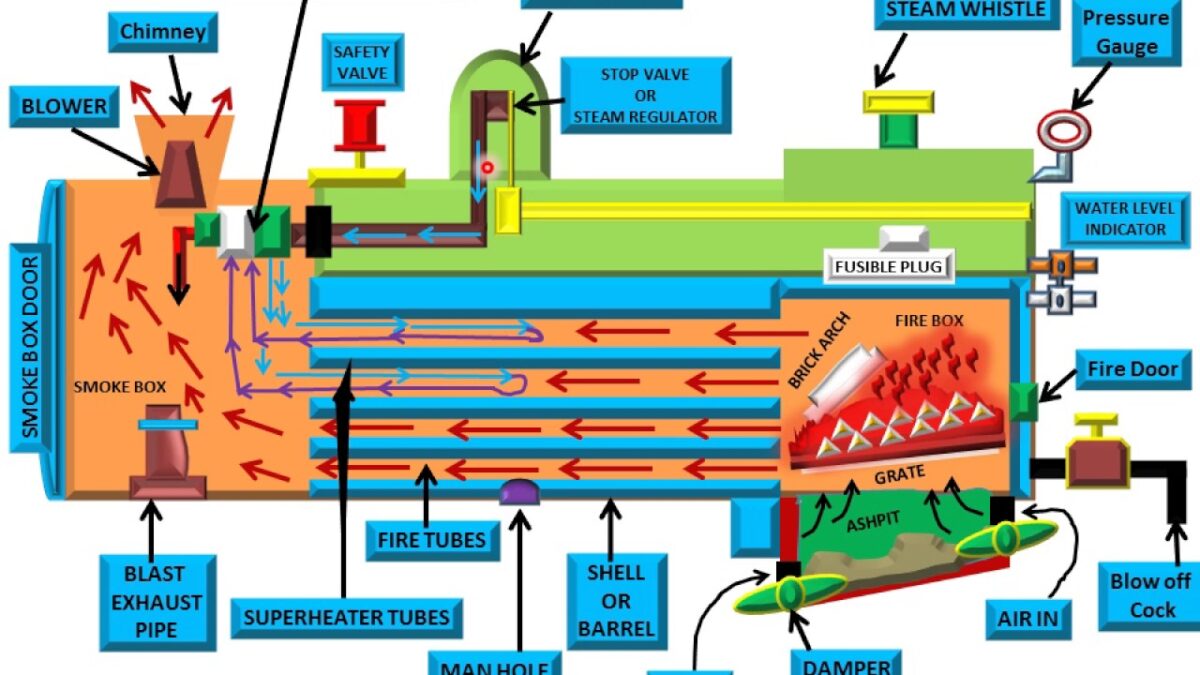
Components of the Locomotive Boiler
The main components of building a locomotive boiler are the following:
- Fire hole
- Firebox
- Grate
- Fire brick arch
- Boiler tubes
- Smokebox
- Blast pipe
- Steampipe
- Dome
- Superheater element pipe
- Superheater header
- Chimney
Let’s see the details of each parts one by one.
- Fire hole
It is a hole provided at the rear end of the boiler. Solid fuel is added to the furnace through this fire hole.
- Fire box
A firebox is a type of box where fuel is burned.
- Grate
A grate is a stage where solid fuel is stored and burned.
- Fire brick arch
An arch of fire bricks is placed on a slope over the grate. It Prevents dust, ash, and particles of burning fuel from entering into the fire tubes. This arch provides a way for the exhaust gases to move in a straight line before entering the fire tubes in the boiler.
- Boiler tubes
They are tubes of fire through which gases emit hot air and exchange heat with the surrounding water.
- Smoke box
According to its name, it is a box in which the smoke of a burnt fuel (gasoline) is collected after passing through the fire tubes. From there it is exhausted to the atmosphere through the chimney.
- Blast pipe
It is a pipe provided over the steam engine. The exhaust system passes through this blast pipe. It is used to create artificial draft that exhaust fumes through a chimney and to create the absorption of hot gases. Created absorption allows gases to emit hot air through the combustion channels.
- Steampipe
It is a pipe through which steam passes. We have two steam pipes, one of which is a large steam pipe located between the head of the superheater and dome. And the second one is the one that connects the superheater exit to the steam engine.
- Dome
It is located at the top and contains a steam controller produced through a steam pipe.
- Superheater feature pipes
These are the superheater pipes where the steam travels and become superheated.
- Superheater Header
It is the head of the superheater that receives steam from the steam pipe.
- Chimney
It is used to emit smoke and gases in the surrounding environment. The chimney length is too small for this boiler.
Working Principle of Locomotive Boiler
In a locomotive boiler, first, solid fuel (coal) is put into the grate and burned from the fire hole. Fuel combustion starts and creates hot gases. An arch of fire bricks is provided that enables the flow of hot exhaust gases in a definite path (straight line) before entering long tubes (fire tubes). It also prevents the ingress of solid fuel particles into the fire tubes.
The hot exhaust gases pass through long fire tubes and heat the water around them. Due to the heat, the water is converted into saturated steam and collected at the top.
The saturated steam from the dome enters the steam pipe with the help of a control valve. The steam runs through a main steam pipe and reaches the superheater header. From the header, the steam goes into the superheater element (feature) pipes.
Here it is very hot i.e. superheated and the superheated steam enters the steambox pipe. The steam from the superheater will go the cylinder containing the piston. The superheated steam causes the piston to move inside the cylinder.
The piston is connected to the wheels of the steam engine and the wheels begin to rotate. An exhaust fumes from the cylinder enter the blast pipe.
Burning gases and smoke after passing through the fire tubes enter the smoke box. An exhaust steam coming from an blast pipe pushes smoke out of a boiler through a chimney.
Here the smoke cannot escape from the boiler itself, so the artificial draft is made by steam from the steam engine. These artificial drafts pushes the smoke out of the smokebox and cause the absorption of hot gases.
Advantages of Locomotive Boiler:
• It is absolutely portable.
• This boiler is able to meet the needs of a fast and flexible system.
• It is an cost effective boiler.
• High level of steam generation.
• It is compact in size and easy to operate.
Disadvantages of Locomotive Boiler:
• It faces problems with rust and scales.
• Unable to operate under heavy load conditions due to overheating problems.
• Some of its water space is difficult to clean.
• The overall efficiency is low.
Applications of Locomotive Boiler
• Locomotive boilers are used in trains and in marines.
• This type of boiler is used in traction engines.
• This is also used for steam rollers.
• It can be used in portable steam engines and in other steam road vehicles.
That’s all from today’s article. Now its time to wrap up this information. Hope you all like this content. Till then! keep learning and exploring this beautiful engineering world.
FAQ’s:-
Q. Locomotive boiler is a
Multi-tubular, horizontal, internally fired and mobile boiler
Q. Which boiler is best suited to meet the fluctuating demand of steam?
Locomotive boiler
Q. The maximum steam pressure in a Locomotive boiler is limited to
1.8 MN/m^2
Q. Which of these is a mobile boiler?
Locomotive boiler
Q. What are the application of locomotive boiler?
Locomotive boilers are mainly used in trains and in marines.