What is Multi Plate Clutch?
Table of Contents
A multi plate clutch is a type of clutch used in vehicles with manual transmissions. It consists of multiple friction plates that are arranged in an alternating pattern between two rotating members. The clutch is engaged by pressing the clutch pedal, which disengages the friction plates and allows the transmission to be shifted.
When the clutch pedal is released, the pressure on the clutch plates causes them to come together and engage, transmitting power from the engine to the transmission. The more plates a clutch has, the more torque it can transmit without slipping.
Multi plate clutches are commonly used in high-performance vehicles, such as sports cars and racing cars, because they can handle higher torque loads than single-plate clutches. They are also used in heavy-duty applications, such as trucks and buses, where the higher torque capacity is necessary to handle heavy loads.
One advantage of a multi plate clutch is that it can be made smaller and lighter than a single-plate clutch with the same torque capacity. This is because the multiple plates can share the load, reducing the stress on each individual plate.
However, multi plate clutches can be more complex and expensive to manufacture than single-plate clutches. They also require more frequent maintenance and may need to be replaced more often due to the increased wear on the multiple friction surfaces.
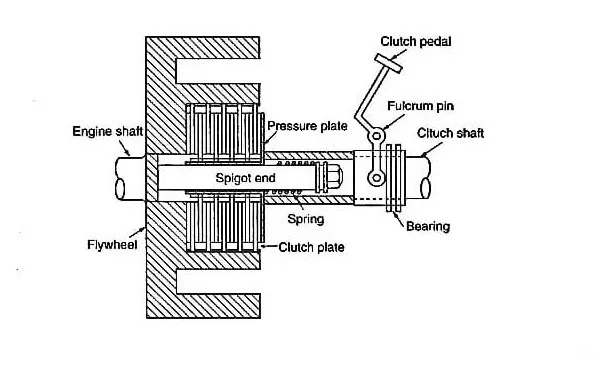
Multi Plate Clutch diagram
Applications of Multi Plate Clutch
Multi plate clutches are widely used in various applications where the transfer of high torque and power is required. Here are some of the applications of multi-plate clutches:
- Automotive vehicles: Multi plate clutches are commonly used in high-performance vehicles, such as sports cars and racing cars. They can handle higher torque loads than single-plate clutches, making them ideal for high-performance applications.
- Heavy-duty trucks and buses: Multi plate clutches are used in heavy-duty applications, such as trucks and buses, where the higher torque capacity is necessary to handle heavy loads.
- Industrial machinery: Multi-plate clutches are used in various industrial machinery applications, such as cranes, winches, and hoists, where high torque transfer is required.
- Marine propulsion: Multi-plate clutches are used in marine propulsion systems, such as boats and ships, where high torque transfer and reliable operation are required.
- Aircraft engines: Multi-plate clutches are also used in aircraft engines, where they are used to connect and disconnect the engine from the propeller during takeoff and landing.
Multi Plate Clutch Construction
A multi-plate clutch consists of the following components:
- Flywheel: The flywheel is a heavy circular disc mounted on the engine’s crankshaft that stores rotational energy. It is attached to one side of the clutch assembly.
- Pressure plate: The pressure plate is a flat circular disc that is mounted to the flywheel. It applies pressure to the clutch plates to engage them when the clutch pedal is released.
- Friction plates: The friction plates are flat discs that are sandwiched between the flywheel and pressure plate. They have a high-friction surface on both sides to transmit power and torque from the engine to the transmission.
- Clutch hub: The clutch hub is located in the center of the clutch assembly and is connected to the transmission input shaft. It holds the clutch plates in place and allows them to rotate freely.
- Clutch springs: The clutch springs are located between the pressure plate and the clutch hub. They provide the pressure necessary to engage the clutch plates.
- Release bearing: The release bearing is mounted on the clutch fork and engages the pressure plate when the clutch pedal is pressed. It disengages the clutch plates from the flywheel, allowing the transmission to be shifted.
The above components are arranged in an alternating pattern to form the clutch assembly. The friction plates are interleaved between the flywheel and the pressure plate. When the clutch pedal is released, the pressure plate applies pressure to the friction plates, causing them to engage and transmit power from the engine to the transmission. When the clutch pedal is pressed, the release bearing disengages the pressure plate, allowing the friction plates to separate and the transmission to be shifted.
Types of Multi-Plate Clutch
There are different types of multi-plate clutches, including:
- Wet clutch: A wet clutch is a multi-plate clutch that is immersed in oil. The oil cools and lubricates the clutch plates, preventing excessive wear and tear. This type of clutch is commonly used in motorcycles, ATVs, and some high-performance vehicles.
- Dry clutch: A dry clutch is a multi-plate clutch that is not immersed in oil. This type of clutch generates more heat and noise than a wet clutch, and requires more frequent maintenance, but is less expensive to manufacture.
- Dual clutch: A dual clutch is a type of multi-plate clutch that uses two separate clutches, one for even gears and one for odd gears. The clutches work in tandem to allow seamless gear shifts without interrupting power delivery.
- Carbon clutch: A carbon clutch is a multi-plate clutch that uses carbon fiber for the friction plates instead of traditional friction material. This type of clutch is commonly used in high-performance racing vehicles.
- Cone clutch: A cone clutch is a type of multi-plate clutch that uses conical friction plates instead of flat plates. This design provides a larger surface area for friction, allowing for higher torque capacity.
Advantages and disadvantages of a multi-plate clutch
Advantages of a multi-plate clutch:
- High torque capacity: Multi-plate clutches can handle higher torque loads than single-plate clutches, making them ideal for high-performance applications.
- Smooth engagement: Multi-plate clutches provide smooth and progressive engagement, making them easier to use and more comfortable for the driver.
- Durability: The design of multi-plate clutches is more robust and durable than single-plate clutches, making them more resistant to wear and tear.
- Compact size: Multi-plate clutches are more compact and lighter than other types of clutches, making them ideal for applications where space and weight are limited.
Disadvantages of a multi-plate clutch:
- Cost: Multi-plate clutches are more expensive to manufacture than single-plate clutches, which can make them less accessible for some applications.
- Complexity: The design of a multi-plate clutch is more complex than a single-plate clutch, which can make maintenance and repairs more challenging.
- Heat generation: Multi-plate clutches generate more heat than single-plate clutches, which can cause overheating and premature wear of the friction material.
- Noise: Multi-plate clutches can generate more noise than other types of clutches, which can be a nuisance for some applications.
Conclusion for Multi Plate Clutch
In conclusion, a multi-plate clutch is a type of clutch used in manual transmissions of vehicles that utilizes several alternating friction discs and steel plates. This design allows for a higher level of torque capacity and heat dissipation, making it ideal for high-performance applications. When the clutch pedal is pressed, hydraulic pressure is applied to the clutch plates, causing the friction discs to engage with the steel plates and lock the clutch to the flywheel of the engine, allowing the transmission to transfer power to the wheels. When the clutch pedal is released, the pressure is released, and the clutch disengages from the engine, allowing it to spin freely and disengage the engine from the transmission.
You may also like this-